Understanding the Difference Between AI, ML, and Deep Learning
The tech world is buzzing with terms like AI, ML, and Deep Learning, but what do they really mean? While these technologies are interconnected, each plays a distinct role in shaping our digital future.
In this blog, we'll break down the key differences between Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning. You'll learn about their definitions, real-world applications, and understand how they work together. We'll explore each concept's advantages and disadvantages, and see how they compare through practical examples.
Ready to clarify these often-confused concepts? Let's dive in!
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Definition: AI is the broadest concept, referring to the ability of machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This includes reasoning, learning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding.
Example: Think of AI as a smart assistant that can play chess, recommend movies, or even drive a car. It encompasses various technologies and approaches.
Advantages
Versatility: AI can be applied in numerous fields, from healthcare to finance.
Efficiency: AI can process vast amounts of data quickly, making it invaluable for decision-making.
Disadvantages
Complexity: Developing AI systems can be complicated and resource-intensive.
Ethical Concerns: Issues like job displacement and privacy arise with AI implementation.
Next Up: Now that we understand AI, let’s dive into Machine Learning, a subset of AI.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Definition: Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. Instead of being explicitly programmed for every task, ML systems learn from experience.
Example: Imagine a spam filter in your email. It learns from the emails you mark as spam and gradually improves its ability to filter out unwanted messages.
Advantages
Adaptability: ML systems improve over time as they are exposed to more data.
Automation: They can automate decision-making processes, reducing human intervention.
Disadvantages
Data Dependency: ML requires large amounts of data to learn effectively.
Black Box Issue: Sometimes, it can be unclear how ML models arrive at their conclusions.
Next Up: With ML in mind, let’s explore Deep Learning, which is a more advanced form of ML.
Suggested Reads - What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
3. What is Deep Learning (DL)?
Definition: Deep Learning is a specialized subset of ML that uses neural networks with many layers (hence "deep") to analyze various factors of data. It mimics the way the human brain works, allowing for more complex data processing.
Example: Think of facial recognition technology. DL algorithms can identify and verify faces in photos by analyzing patterns in pixel data.
Advantages
High Accuracy: DL can achieve remarkable accuracy in tasks like image and speech recognition.
Feature Extraction: It automatically identifies the features that are important for making predictions, reducing the need for manual feature engineering.
Disadvantages
Resource Intensive: DL requires significant computational power and large datasets.
Less Interpretability: The complexity of DL models can make it difficult to understand how they work.
Now that we’ve covered the basics of AI, ML, and DL, let’s compare them directly.
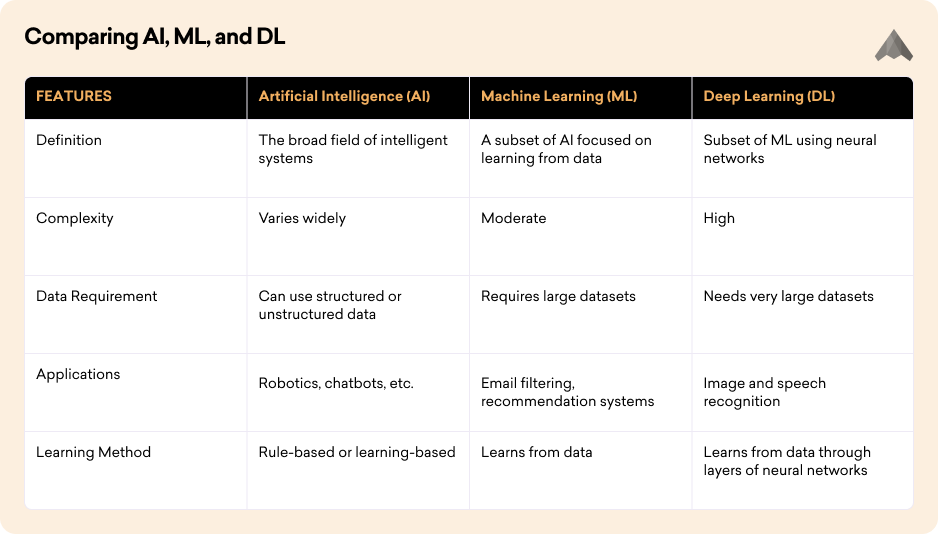
Comparing AI, ML, and DL
Suggested Reads- How To Use Open Source LLMs (Large Language Model)?
Our Final words
AI is the overarching field that encompasses both ML and DL. ML is a method within AI that allows systems to learn from data, while DL is a more advanced method that uses neural networks to learn from large amounts of data. Understanding these distinctions helps us appreciate how these technologies work together to create intelligent systems that can enhance our lives.
As we move forward, the integration of AI, ML, and DL will continue to shape the future of technology, offering exciting possibilities and challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What's the minimum computing power needed for Deep Learning?
Deep Learning typically requires high-performance GPUs, significant RAM (16GB+), and modern multi-core processors for efficient model training and deployment.
2. Is Machine Learning the same as AI?
No. Machine Learning is a subset of AI focusing specifically on algorithms that learn from data, while AI is the broader field of making machines intelligent.
3. Can Deep Learning work without the internet?
Yes. Once trained, Deep Learning models can run offline. However, internet connectivity may be needed for model updates or cloud-based processing.
