Composable Commerce vs Headless: Which is Better?
If you're scratching your head wondering about composable commerce vs headless e-commerce, you're not alone. These terms get thrown around a lot, but understanding their real-world impact isn't always straightforward.
In this guide, we'll cut through the jargon and break down what these approaches actually mean for your online store. Whether you're a small business owner or running a large e-commerce operation, we'll help you figure out which path might be the best fit for your unique needs.
What is Headless Commerce?
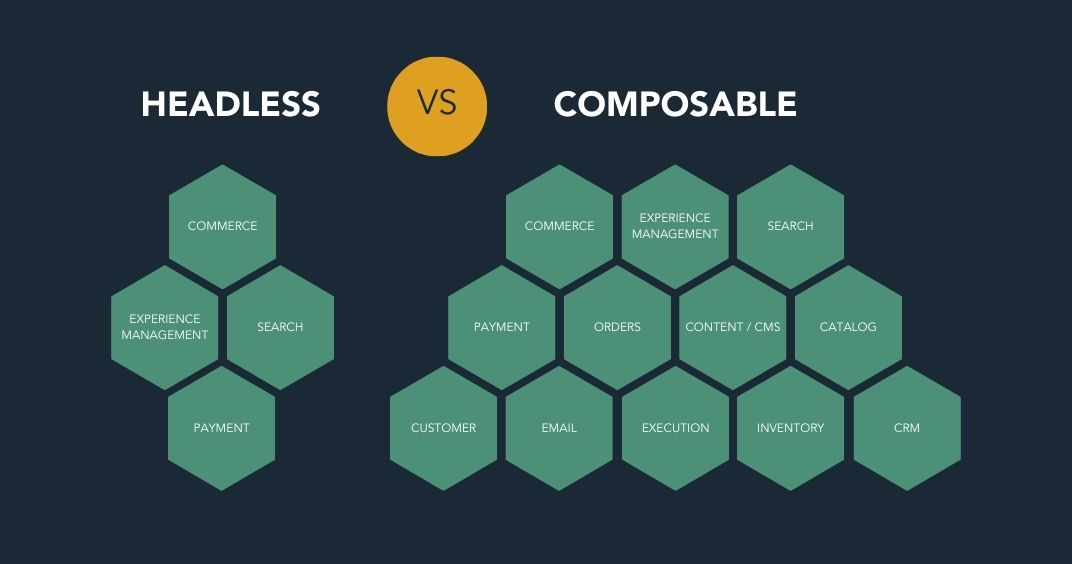
Headless commerce is an e-commerce architecture where the front-end presentation layer (the "head") is decoupled from the back-end e-commerce functionality. This separation allows for greater flexibility in designing the user interface and enables businesses to deliver content across various channels and devices.
What is Composable Commerce?
Composable commerce takes the concept of headless a step further. It's an approach where the entire e-commerce stack is broken down into modular components that can be selected, assembled, and reassembled as needed. This allows businesses to create a custom e-commerce solution by choosing the best-of-breed components for each function.
Differences Between Headless vs Composable Commerce
While both approaches offer flexibility and customization, there are several key differences between headless and composable commerce:
- Architecture
- Headless: Separates the front end from the back end.
- Composable: Breaks down the entire e-commerce stack into modular components.
- Flexibility
- Headless: Offers flexibility in the front-end design and content delivery.
- Composable: Provides flexibility across the entire e-commerce ecosystem.
- Customization
- Headless: Allows for customized front-end experiences.
- Composable: Enables customization of both front-end and back-end components.
- Integration
- Headless: Typically requires integration with a single back-end system.
- Composable: Allows for integration of multiple best-of-breed components.
- Scalability
- Headless: Scales well for front-end needs.
- Composable: Offers scalability across all aspects of the e-commerce platform.
Advantages of Headless Commerce
When considering headless vs composable commerce, it's important to understand the benefits of each approach. Here are some advantages of headless commerce:
- Improved Front-End Flexibility: Developers can use any front-end technology to create unique user experiences.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Changes to the front end can be made quickly without affecting the back end.
- Omnichannel Readiness: Content can be easily distributed across multiple channels and devices.
- Better Performance: The decoupled architecture can lead to faster page load times.
- Enhanced SEO: Developers have more control over on-page SEO elements.
Suggested Reads- Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Your Headless Shopify Store
Advantages of Composable Commerce
Now, let's look at the benefits of a composable commerce platform:
- Ultimate Flexibility: Businesses can choose the best components for each function, creating a truly custom solution.
- Future-Proofing: As new technologies emerge, individual components can be replaced without overhauling the entire system.
- Scalability: Each component can be scaled independently as needed.
- Best-of-Breed Integration: Companies can leverage the best solutions for each aspect of their e-commerce operations.
- Rapid Innovation: New features and capabilities can be added quickly by integrating new components.
Challenges of Headless Commerce
While headless commerce offers many benefits, it also comes with some challenges:
- Increased Complexity: Managing separate front-end and back-end systems can be more complex than traditional e-commerce platforms.
- Potential Higher Costs: The initial setup and ongoing maintenance may require more resources.
- Reliance on APIs: The system heavily relies on APIs, which need to be well-managed and secured.
- Back-End Limitations: While the front-end is flexible, businesses are still constrained by the capabilities of the chosen back-end system.
Challenges of Composable Commerce
Similarly, composable commerce has its own set of challenges:
- Integration Complexity: Ensuring all chosen components work seamlessly together can be challenging.
- Vendor Management: Working with multiple vendors for different components can be time-consuming.
- Expertise Required: Implementing and managing a composable system requires a high level of technical expertise.
- Potential for Overengineering: There's a risk of creating an overly complex system by trying to compose too many specialized components.
Composable Commerce vs Headless: Which to Choose?
The choice between composable commerce vs headless depends on various factors:
Consider Headless If:
- You primarily need front-end flexibility.
- You're satisfied with your current back-end system but want to improve the user interface.
- You want to improve your omnichannel capabilities.
- You have a team comfortable with API-driven development.
Consider Composable If:
- You need flexibility across your entire e-commerce ecosystem.
- You want to leverage best-of-breed solutions for different functions.
- You have complex, unique business requirements that off-the-shelf solutions can't meet.
- You have the technical resources to manage a more complex, modular system.
Implementing Headless Commerce
If you decide to go the headless route, here are some steps to consider:
- Choose a Back-End System: Select a robust e-commerce platform that offers strong API capabilities.
- Select Front-End Technologies: Decide on the front-end frameworks and tools that best suit your needs.
- Plan Your API Strategy: Determine how your front end will communicate with the back end through APIs.
- Develop Custom Front-End: Create your unique user interface and experience. This is where headless e-commerce development services can be particularly valuable, ensuring seamless integration between your front-end and back-end systems.
- Integrate and Test: Ensure seamless communication between the front-end and back-end systems.
Implementing Composable Commerce
If composable commerce seems right for your business, consider these steps:
- Assess Your Needs: Identify the key components you need for your e-commerce operations.
- Research and Select Components: Choose the best-of-breed solutions for each aspect of your e-commerce stack.
- Plan Integration: Determine how all the chosen components will work together.
- Implement Incrementally: Start with core components and gradually add others to minimize disruption.
- Continuous Optimization: Regularly assess and upgrade components as needed to maintain a cutting-edge system.
Suggested Reads- Reasons To Choose Headless Shopify
Our Final Words
In the debate of composable vs headless, there's no one-size-fits-all answer. Both approaches offer significant advantages over traditional monolithic e-commerce platforms, providing greater flexibility, scalability, and customization.
Headless commerce offers a straightforward way to improve front-end experiences and omnichannel capabilities, making it a good choice for businesses looking to enhance their current e-commerce setup.
On the other hand, a composable commerce platform provides the ultimate in flexibility and customization, allowing businesses to create truly unique e-commerce ecosystems tailored to their specific needs.
Ultimately, the choice between composable and headless commerce depends on your business requirements, technical resources, and long-term e-commerce strategy. By carefully considering the pros and cons of each approach, you can make an informed decision that will position your business for e-commerce success in the years to come.
Need Expert Help?
F22 Labs offers expert headless e-commerce development services to transform your online presence. Our skilled team specializes in creating custom, high-performance headless solutions that drive growth and enhance user experience. Let us help you navigate the complexities of modern e-commerce and build a system tailored to your unique business needs.
Frequently asked questions
Q1. What's the main difference between composable commerce and headless e-commerce?
Headless separates the front-end from a single back-end, while composable breaks down the entire e-commerce stack into modular components. Composable offers more flexibility across the whole ecosystem, whereas headless focuses on front-end flexibility.
Q2. Is composable commerce more expensive than headless?
Composable commerce can be more expensive initially due to its complexity and the need to integrate multiple components. However, long-term costs may be lower as you can easily replace or upgrade individual components as needed.
Q3. Can a business transition from headless to composable commerce?
Yes, transitioning from headless to composable commerce is possible. It involves breaking down the back-end into modular components and may require replacing some existing systems. The transition should be planned carefully to minimize disruption.
